The CDM Regulations – what you need to know
The Construction (Design and Management) Regulations were introduced in 1994 to improve the health and safety of construction projects. The CDM regulations were revised a few times since they were first devised, but they still have the same purpose — to ensure the safety and welfare of everyone involved.
The latest changes to CDM in construction were in 2015, so the regulations we know and adhere to now are known as the CDM Regulations [2015], or CDM 2015 for short.
Below we’ve summarised the key points to illustrate what the CDM Regulations are – why they’re important – and how you can make sure that your projects are compliant.
Why are the CDM Regulations important?
Construction is one of the most dangerous industries in the UK. Statistics show that every year, tens of thousands of construction workers suffer from work-related ill-health or serious injury. What’s more, the fatal injury rate in the construction industry is three times higher than that across all other industries.
By adhering to CDM Regulations, construction companies and contractors can ensure that risk is kept to a minimum and that workers, occasional staff and site visitors are also protected from harm.
Complying with these regulations is also a legal requirement.
Every construction project must meet specific requirements as detailed in CDM 2015.
A summary of the CDM Regulations
The Construction (Design and Management) Regulations outline a number of steps that should be taken to ensure risk is effectively managed throughout construction projects.
The three main CDM roles are CDM Client, CDM Designer and CDM Contractor.
For projects involving more than one contractor, the additional roles of Principal Designer (PD) and Principal Contractor (PC) are required to plan, manage, monitor and coordinate the work.
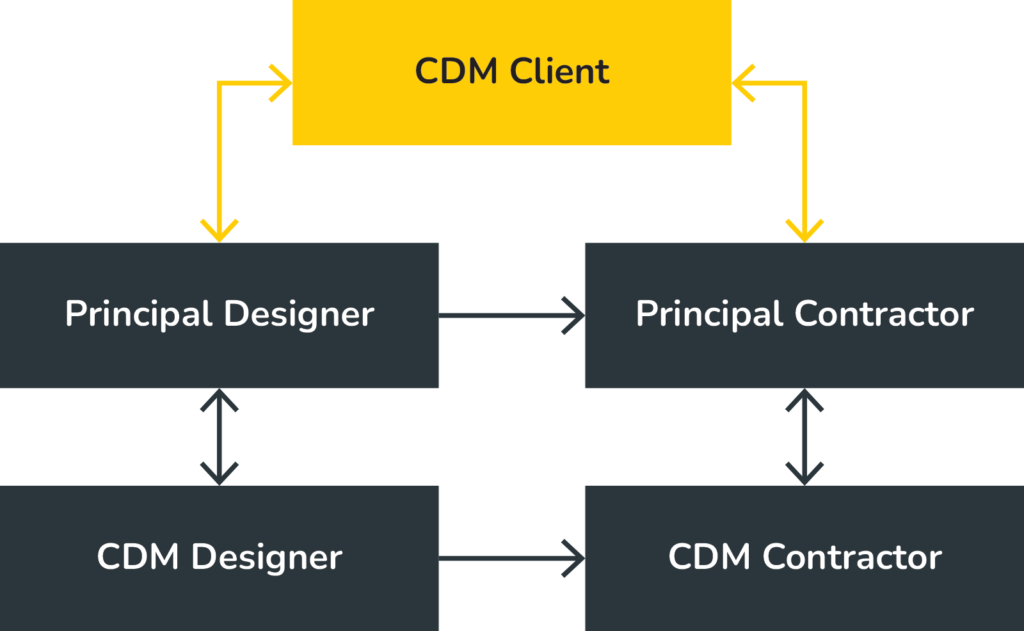
These health and safety responsibilities and project duties are divided between the respective “duty holders”, comprising the individuals involved in the construction project – such as the clients, designers, contractors and workers.
Client Responsibilities
- Appointing project roles
- Preparing a Client brief
- Ensuring sufficient time and resources
- Providing pre-construction information
- Notifying the HSE when the criteria are met
Principal Designer Responsibilities
- Helping the Client set up the project
- Advising the Client on time and resources required
- Assisting the Client to collate pre-construction information
- Identifying and eliminating foreseeable risks
- Liaising with the Principal Contractor and other Designers
- Taking charge of the Health and Safety file
Principal Contractor Responsibilities
- Considering all Health and Safety risks
- Liaising with the Client and Principal Designer
- Preparing a Construction Phase Plan
- Providing suitable welfare facilities
- Managing contractors and other workers
Designer Responsibilities
- Referring to pre-construction information, ensure the Client knows their responsibilities when preparing or modifying designs
- Considering risks during design creation process
- Providing design information as required
Contractor Responsibilities
- Ensure Clients know and understand their responsibilities
- Managing workers and other staff
- Preventing access to unauthorised persons


















